Hideen Number 52 : Visual perception challenges have captivated human minds for centuries, and modern optical illusions continue to test our cognitive abilities in fascinating ways.
The latest brain teaser making waves across social media platforms presents a deceptively simple yet remarkably challenging task: locating a single correctly oriented number 52 hidden within a grid of inverted 52s, all within the span of just seven seconds.
This particular visual puzzle exemplifies how our brains process information and highlights the intricate relationship between perception, attention, and pattern recognition.
What appears straightforward at first glance quickly reveals itself as a sophisticated test of visual acuity and mental processing speed.
The Science Behind Visual Perception Challenges
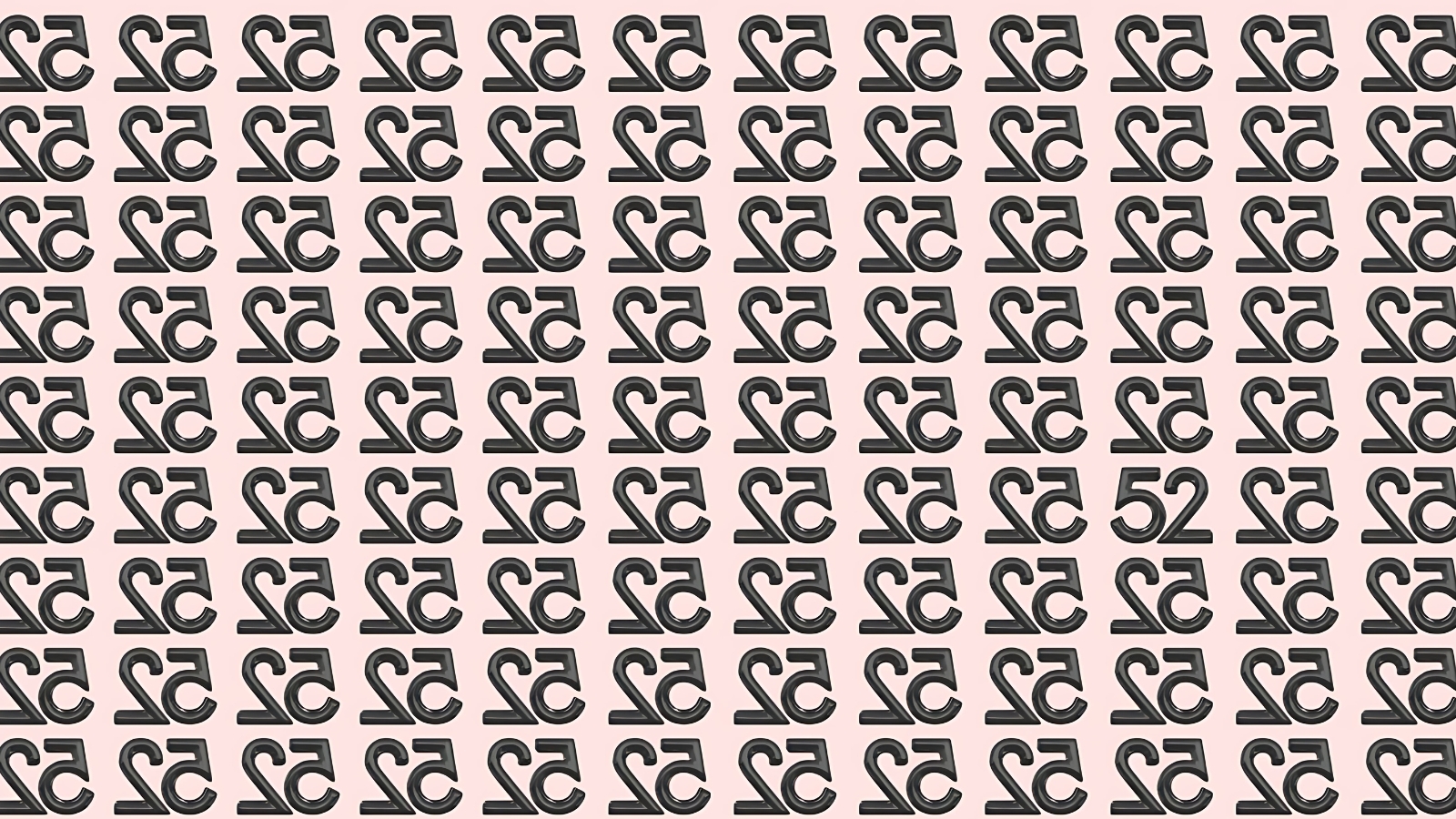
Understanding why these optical illusions prove so challenging requires examining how our visual system processes information.
When we look at a grid filled with similar-looking numbers, our brain attempts to categorize and organize the visual input efficiently.
This process, known as pattern recognition, typically helps us navigate the world quickly and effectively.
However, when confronted with subtle variations like inverted numbers, our visual system can become overwhelmed by the sheer volume of similar stimuli.
The brain’s tendency to group similar objects together, a principle known as the Gestalt theory of perception, actually works against us in this scenario.
Instead of examining each number individually, our minds try to process the entire grid as a unified pattern.
The challenge becomes even more complex when time pressure enters the equation. Seven seconds may seem like a reasonable timeframe, but under pressure, our visual scanning patterns often become less systematic and more erratic.
This rushed examination can cause us to overlook the very detail we’re searching for, even when it’s hiding in plain sight.
Neurological Mechanisms at Work
Visual Processing Pathways
The human visual system employs two primary pathways for processing information: the dorsal stream and the ventral stream.
The dorsal stream, often called the “where” pathway, processes spatial relationships and movement, while the ventral stream, known as the “what” pathway, handles object recognition and identification.
In this optical illusion challenge, both pathways work simultaneously. The dorsal stream helps us scan across the grid systematically, while the ventral stream attempts to distinguish between the inverted and correctly oriented numbers.
The competition between these two systems under time pressure creates the cognitive difficulty we experience.
Attention and Focus Mechanisms
Selective attention plays a crucial role in solving visual puzzles like this one. Our brains possess limited processing capacity, forcing us to allocate attention strategically.
When faced with a grid of similar numbers, we must decide whether to employ focused attention on individual elements or distributed attention across the entire field.
Research in cognitive psychology suggests that the most effective approach combines both strategies.
Initially scanning the entire grid with distributed attention can help identify potential areas of interest, followed by focused examination of specific regions where the target might be located.
Strategies for Improving Visual Perception
Systematic Scanning Techniques
Developing effective scanning patterns can significantly improve performance on visual challenges.
Rather than allowing your eyes to dart randomly across the grid, implement a systematic approach such as scanning from left to right, top to bottom, or following a spiral pattern from the outside inward.
Professional fields that require exceptional visual acuity, such as radiology and air traffic control, employ specific training techniques to enhance pattern recognition abilities.
These methods can be adapted for recreational visual challenges, improving both speed and accuracy.
Mental Preparation Strategies
Before attempting the challenge, take a moment to visualize what you’re looking for. Form a clear mental image of the correctly oriented number 52, paying particular attention to the specific features that distinguish it from its inverted counterparts.
This mental preparation helps prime your visual system for the specific target you need to identify.
Additionally, controlling your breathing and maintaining a relaxed state can improve visual processing efficiency.
Tension and anxiety can impair cognitive function, making it more difficult to maintain the focused attention required for these challenges.
The Role of Practice and Experience
Neuroplasticity and Visual Training
Regular engagement with visual perception challenges can lead to measurable improvements in processing speed and accuracy.
This improvement occurs through neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new neural connections in response to experience.
Studies have shown that individuals who regularly practice visual discrimination tasks develop enhanced abilities in related areas, including improved attention control, faster processing speeds, and better pattern recognition capabilities.
These benefits extend beyond recreational puzzles into practical applications in daily life.
Progressive Difficulty Levels
For those looking to improve their visual perception skills, starting with simpler challenges and gradually increasing difficulty provides the most effective training approach.
Begin with larger grids containing fewer distractors, then progress to more complex arrangements with subtle variations and shorter time limits.
Cognitive Benefits of Visual Challenges
Enhanced Attention Control
Regular practice with optical illusions and visual puzzles can strengthen attention control mechanisms. These exercises train the brain to maintain focus while filtering out irrelevant information, a skill that proves valuable in numerous real-world situations.
Improved Processing Speed
The time pressure inherent in these challenges forces the brain to process information more efficiently. Over time, this can lead to improvements in general cognitive processing speed, benefiting tasks ranging from reading comprehension to decision-making.
Pattern Recognition Development
Visual challenges enhance the brain’s ability to identify patterns and relationships between different elements.
This skill proves particularly valuable in fields requiring data analysis, problem-solving, and creative thinking.
The Psychology of Time Pressure
Stress Response and Performance
The seven-second time limit creates a mild stress response that can either enhance or impair performance, depending on the individual’s stress tolerance and experience level.
Understanding this relationship helps explain why some people thrive under pressure while others struggle.
Optimal Challenge Levels
Psychological research suggests that moderate levels of challenge and time pressure can enhance performance by increasing focus and motivation.
However, excessive pressure can lead to anxiety and decreased performance, highlighting the importance of finding the right balance.
Cultural and Individual Variations
Cultural Differences in Visual Processing
Research has revealed interesting cultural variations in visual processing preferences. Some cultures emphasize holistic processing, viewing scenes as unified wholes, while others focus more on analytical processing, examining individual components separately.
Individual Differences in Cognitive Style
People vary significantly in their preferred cognitive styles, with some individuals naturally excelling at detail-oriented tasks while others perform better with big-picture thinking.
Understanding your personal cognitive style can help you develop more effective strategies for visual challenges.
Practical Applications
Professional Benefits
The skills developed through visual perception challenges have practical applications in various professional fields. Medical professionals, security personnel, quality control inspectors, and many other occupations rely heavily on visual discrimination abilities.
Educational Value
These challenges serve as excellent educational tools for teaching principles of perception, attention, and cognitive psychology. They provide concrete examples of abstract concepts while engaging learners in active participation.
Optical Illusion Answer
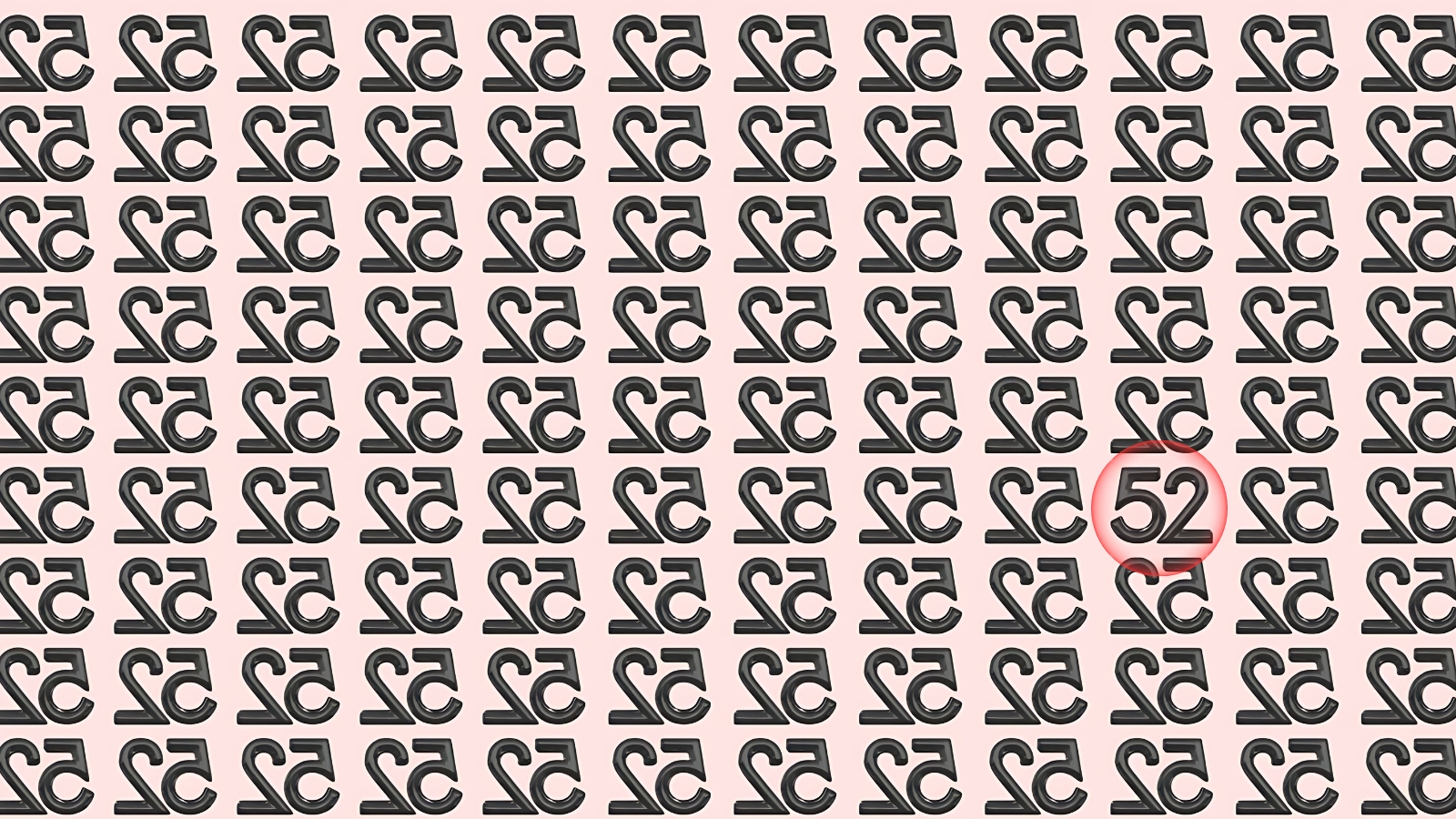
The optical illusion challenge of finding the hidden number 52 among inverted variants represents far more than a simple entertainment activity.
It serves as a window into the complex mechanisms of human perception and cognition, offering insights into how our brains process visual information under pressure.
Whether you successfully locate the target within seven seconds or require additional time, the attempt itself provides valuable exercise for your visual processing systems.
Regular engagement with such challenges can lead to measurable improvements in attention, processing speed, and pattern recognition abilities.
The next time you encounter this or similar visual puzzles, remember that the real value lies not just in solving the challenge, but in understanding the remarkable cognitive processes that make such problem-solving possible
. These insights can enhance your appreciation for the incredible complexity and capability of the human visual system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why do optical illusions like this one seem so difficult despite appearing simple? A: The difficulty arises from our brain’s tendency to process similar visual elements as patterns rather than examining each item individually.
The inverted numbers create visual confusion that challenges our normal pattern recognition processes.
Q: Can regular practice with visual challenges actually improve my perception skills? A: Yes, research shows that consistent practice with visual discrimination tasks can enhance attention control, processing speed, and pattern recognition abilities through neuroplasticity.
Q: What’s the best strategy for solving this type of optical illusion quickly? A: Use systematic scanning patterns rather than random searching, maintain relaxed focus, and mentally prepare by visualizing the target before beginning the challenge.